Debugging KDE4 Plasmoids
by admin on Mar.12, 2010, under Linux
So you have downloaded that spiffy new plasmoid for KDE4 and installed it. Then all manner of interesting things begin to occur. Perhaps the new plasmoid itself simply does not function correctly, or perhaps the next time you login the plasma desktop fails to start. Or, in my most recent case, configuring the plasmoid caused a seg fault which then crashed the entire plasma desktop. Ahh, such pleasant surprises. I’ve never really taken on learning the first thing about plasmoids really – it’s been on the list, but pretty low. However, this most recent situation of a crashing desktop on login inspired me to at least dip my toe.
While there is certainly much more to know, and while I am not a developer, I thought it might be helpful to point out a few things that may help others with crashing plasmoids. I’ll add to this as I learn more, but this should at least point you in the right direction. I was suprised that googeling for debugging plasmoids returned rather dismal results, and no guide appears readily available, so if you have landed here, good luck and please add your own hints.
Okay – so first off, some basics. If your KDE desktop has crashed, don’t panic. You can actually restart it easily enough. First, try alt tabbing to see if your windows are sill running despite the inhospitable and otherwise completely black screen. Start Konsole using Krunner (alt-f2) and once at the command line simple restart the process:
paracelsus@Callandor:~> plasma-desktop
That should re-initiate your desktop. (If your X server was killed as well, then the issue is not as likely with the plasmoid, and you may have other things going on. If X dies and dumps you to the shell you can usually restart it by running startx If X is still running, but you can’t start Krunner and Konsole, simply go out to a virtual terminal (ctrl-alt-f1) and restart plasma-desktop )
Of course, if you have a buggy plasmoid that is crashing, it may very well just crash again. If you just installed the faulty plasmoid and know which one it is you can remove it with:
paracelsus@Callandor:~>plasmapkg -r buggyPlasmoid
(If you don’t know the exact name, try plasmapkg –list)
One other very fine tool is plasmoidviewer. Using this you can run a buggy plasmoid in a more contained environment. This makes it a bit easier to capture output and if it crashes, it likely will not take down the plasma desktop process.
paracelsus@Callandor:~>plasmoidviewer buggyPlasmoid
Now, if that does not work, and your desktop is still crashing, you can try a more drastic fix which is to simple move your KDE user profile. Do so with:
paracelsus@Callandor:~>mv ~/.kde ~./kde-broken
Then, restart X (crtl-alt-backspace) and log in again. This will create a new, default profile. You can then continue troubleshooting the old one, etc.
Also, if you have encountered a buggy plasmoid, please take the time to submit your findings to the author, perhaps at kde-look.org or wherever else you obtained the plasmoid from. Supply the output obtained by running the plasmoid with plasmoidviewer as well as your distro version, kernel, and KDE version as a minimum.
Good luck and if you have any other basic plama / plasmoid trouble shooting tips, please feel free to add them.
Simple SSH Pass Phrase Manager for KDE4
by admin on Feb.20, 2010, under Uncategorized
I’ve finally gotten around to using ssh pass phrases on the ssh keys I uses to authenticate with, and recently was using a nifty applet on Gnome that managed the pass phrase for you when you log into your Gnome session.
Since I mainly use KDE, I found a very simple little app mentioned on this blog that does the same thing for KDE4, ksshaskpass which you can get from here
Compiling and installing is extremely easy, it is a very light app and uses cmake for the build, and builds in seconds.
(Note however that you need to have cmake installed, and if using Ubuntu you also install build-essential and kdelibs5-dev if using KDE.)
Also, please see the readme describing the script to make in your ~/.kde4/Autostart directory setting your SSH_ASKPATH variable to point to the ksshaskpath binary.
After that you are good to go – when you first use your key a GUI window prompts you once for the password, which gets associated with your Kwallet for the remainder of your session.
Very nice.
PHPChain Password Manager
by admin on Feb.19, 2010, under Linux, My Life
NOTE: Since the original post I discovered a new version of PHPChain is available at the project Sourceforge site here. You may test drive it here. The new version has several additional features and the issues with the underlying PHP code described below have been corrected. I had no issues running the new version with PHP 5.3. Unfortunately, there is no way to easily migrate your database from the old version, but the new version does allow the import and export of data in XML format.
PHPChain is a great little app which helps you organize passwords. It uses a web interface, encrypts the passwords in a MySQL database, and supports multiple users, each with their own account. Passwords are organized in user defined groups, and are easy to edit. It automatically alphabetizes entries, helping to organize them further. The interface is extremely easy to use, and it makes storing and organizing you many passwords very easy. You can try a demo of it here.
I opted for this as a solution to store my passwords at home. It provided the added benefit of having access to my passwords from anywhere over an SSL web site. While there may be some slight risk in this, lets be honest — it is a hell of a lot better than the open office document I was using before. And of course you can further protect it by only opening the port it listens on when needed, and even place it behind an .htaccess, etc. You can be as paranoid as you like.
The one thing is that this application does not appear to have been updated in a while, and if you install it today you may run into a situation where PHP does not read some of the scripts as the author used php short tags
Here are some notes that might help you with your install.
First of course you will need to install apache with the necessary php and ssl packages, as well as php5-mcrypt installed. You will also need to generate a self signed SSL certificate and set up a vhost that will accept SSL connection. You certainly want to use SSL, even if you intend to only access this on you local network as otherwise all traffic will be sent clear text, which would be bad. Setting up apache to use a self signed SSL is pretty straight forward and there are lots of sites for your distro to guide you in this.
At a minimum you will need things like:
apache2-2.2.13-2.3.1.i586
apache2-mod_php5-5.3.0-2.4.3.i586
openssl-0.9.8k-3.4.i586
apache2-mod_php5-5.3.0-2.4.3.i586
php5-mcrypt installed
php5-mysql-5.3.0-2.4.3.i586
Once you download PHPChain, simply extract it in your web document root and create and empty MySQL database, them import the .sql file into it. See the README.txt for details. If you access it now, you will likely see lots of messages as some scripts are not being parsed correctly due to the short tags being used. Find which ones this are by:
Callandor:/srv/www/htdocs/phpchain # grep -R ” ./cat.php: ./inc/menu.php: ./inc/db.php: ./inc/cookie.php: ./inc/header.php: ./inc/header.php:PHPChain – Powered by PHPChain
./inc/header.php: ./inc/header.php: ./inc/header.php: ./inc/header.php: ./inc/crypt.php: ./inc/form.php: ./index.php: ./login.php: ./logout.php: ./newlogin.php: ./password.php: ./settings.php:
Change all instances of the
Callandor:/srv/www/htdocs/phpchain # sed “s/> testchange; sed “s/> testchange
To virst view the changes in each file, and then if it looks good replace with:
Callandor:/srv/www/htdocs/phpchain # sed -i “s/
Or, to be even fancier with it . . .
Callandor:/srv/www/htdocs/phpchain # for i in `grep -R “
Now, the php should work correctly, but you will likely have some warnings dispalyed at the top of the page regarding some constant variable declarations. You can disable php warning by setting the error_reporting level on a per script basis. Turn off errors and warnings in index.php (before the include statements) by adding:
error_reporting(0);
Or set the error reporting level in you php.ini
That should do it, you an now start using PHPChain to manage your passwords in a more secure way. Do ensure to use SSL, and if you connect without SSL PHPChain conspicuously warns you of the danger of this.
Resizing Default LVM Partitions and Moving /boot
by admin on Jan.23, 2010, under Linux
Standard Disclaimer: This article makes recommendations on using tools to modify your LVM configuration, your /boot partition, kernel and grub. Data corruption from a mangled LVM, or a (temporarily) unbootable system through a corrupted or mis-configured grub, etc. are entirely possible. I am not responsible for any of this. If you have a running system and break it by changing these things, please realize that I am not to blame, nor will I be able to help you fix things. And of course, making complicated changes on a production environment is not advised. However, if you need to migrate to a larger /boot partition the following may help you. If you are unfamiliar with partitioning, LVM and grub, please plan on having a least a few hours to work your way through this the first time. Also, have a Live CD and possibly the SuperGrub CD already available before hand. You may also want to practice on a virtual machine before trying this on a running server, etc. Installing Virtualbox and setting an a test VM takes only minutes and provides a superlative learning environment.
There is only so far you can get with a 69M /boot.
If you are like me, when you last installed your distro you likely decided to go with the proposed LVM layout. Hey, why not right? This way you can more easily change the sizes of your logical volumes, adding more to home, stealing some from that /whatever slice you just never really ended up using. Plus you can always add another physical drive later for juicy (or potentially disastrous, I’ve heard it both ways) multi-volume LVM expansion goodness.
Or perhaps you just said “yea, sure — whatever” on the partitioning steps.
Despite the best, or worst, planning you at times just need to fix what you are left with.
In my case, for some reason know to only God and the face on Mars, when I last installed Suse I accepted the offered LVM layout, and along with the the pathetic 69M /boot partition. Well, as you start to add some other kernels for Xen, the Suse default and desktop kernels, and if you want to keep any old versions of these, or compile your own, you very quickly realize what a mistake you made.
Now, fixing this is not superlatively difficult of course, but there are easy ways and hard ways.
The hard way involves manually shrinking the LVM Volume Group (vg) which also requires shrinking the Logical Volums (lv) which it contains, which of course requires shrinking the filesystems they contain. Oh the pain.
Sun Studio 12 Update 1 Compiler and IDE
by admin on Aug.11, 2009, under IT Adventures, Linux, Sago Labs
Cool News: This post was a blogging contest winner!
Thank you Sun!
Update: What a pleasant surprise to find that my entry for the Sun Studio blogging contest was selected as one of the winners, and announced on the Sun Studio Developers Site. As promised, Sun sent along $500, marking the first money I’ve made with this blog, and while my purpose in blogging is not focused on making money, it nonetheless was a nice side effect. I certainly enjoyed writing about my initial experience with using Sun Studio 12, and to have been selected as one of the contest winners was certainly a bonus. Thank you Sun Microsystems for holding the contest, and of course for making Sun Studio available to the community.
Every now and again I get emails from Sun Microsystems for guides or other promotions for this or that product: ZFS, Solaris containers, DTrace, etc. Some of them are actually quite interesting and it is a list I like being on.
The other day I received an announcement for the release of Sun Studio 12 Update 1. Well, this was perfect as I have been wanting to test drive Sun Studio for a while, and have been meaning to get to it – but it gets even better: they are having a blogging contest and will actually be paying 10 lucky winners who blog about their experience with it!
Well, let’s see: try out and write about a product which I had intended to do anyway, and perhaps win some cash too – how can one possibly go wrong?
Why Try It?
I’m neither a developer nor programmer. If that fits you as well, you might be thinking “So why bother?” Well, like a lot of folks out there who are Linux guys, sysadmin types, etc. I think it is always good to be familiar with available tools. The IDE I’ve used most is vim, and I’ve rarely even used Eclipse. But I, being an adventure loving soul, of course love checking out new things and was particularly interested in the Sun compiler as I wanted to compare its optimizations and the performance of binaries it compiles against the Intel (icc) and GNU (gcc) compilers. I previously wrote on comparing Intel Linux C complier and gcc binaries using the Crafty chess engine and was quite surprised at the benchmark differences, and have since then wanted to see how a Sun compiled binary would compare. So what a perfect opportunity to try it and find out.
Isn’t that a bit nebulous? One could even dare say Geeky?
While benching chess engine binaries might seem somewhat esoteric, it really gives a good idea of the possibilities. Translate this over to compiling your MySQL server or other performance critical app and it starts to get more interesting. In fact you can get MySQL binaries compiled with the Intel compiler for just this reason directly on the MySQL download page. One can’t help but wonder one MySQL binaries compiled with the Sun compiler might perform.
Install Experience
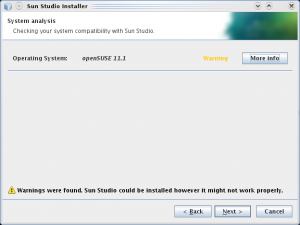
I tested out Sun Studio 12 on both Solaris 10 (2009.06 Nevada) and Linux (Suse 11.1) platforms. In both cases the install was seamless. On Solaris 10 it was simply a matter of using the new IPS packaging system and by running
$ pfexec pkg install sunstudio12u1
it was up and running in minutes.
On the Linux side I downloaded the SunStudio12u1-Linux-x86-rpms.tar.gz package and simply run the install wrapper script, which by default places everything in /opt/sun and the full path to the binary is then /opt/sun/sunstudio12.1/bin/sunstudio (you will need to add that to you PATH environmental.)
The GUI installer which ran in Linux went smoothly and gave basic options for which components to select, etc. You can also install install in non-interactively. The displayed warning was simply saying there was no guarantee it would work on this system (Suse 11.1) – but there were in fact no issues.
The full install (C and Fortran compilers, performance libs and IDE) comes to about 755MB on Linux and about 830Mb on Solaris – a bit larger than I expected.
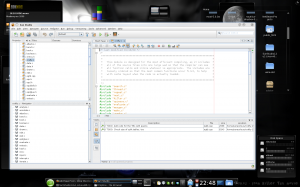
Sun Studio IDE
Launching Sun Studio presents a clean and easy to navigate environment. Though never having used it before, it was pretty obvious where to find things. Several sample projects are available so you can test drive it right away, and there are links to guides presented on the main page. (There is also a comprehensive quick start guide here.)
I did have to play about a bit with adding existing directories of source code into a new project. It is easy enough once you do it. Once you import your source, you can click the build button and you are more or less off.
Of course, you will need to define the full path to the compiler you want to use in the CC= variable in the make file, or have this environmental defined and exported already. If you want to compile with gcc instead, it is no problem – just set cc=gcc In the Crafty make file you can simply set the $(MAKE) linux or $(MAKE) linux-icc to use gcc or icc compilers. I had no difficulty compiling Crafty with gcc this way.
Using the Sun Compiler
As I am utterly unfamiliar with CFlags for the Sun compiler I found it nice that just running the compiler with no arguments immediately tells you how to discover them easily enough with /opt/sun/sunstudio12.1/bin/suncc -flags
I had to figure out the CFLAGS still though, and found this site to be helpful for that.
One I had the correct options set in the Crafty Makefile, the Sun compiler launched into action for me. I used a basic set of CFLAGS:
solaris:
$(MAKE) target=SUN \
CC=/opt/sun/sunstudio12.1/bin/cc CXX='$(CC)' \
CFLAGS='$(CFLAGS) -fast -xO5 -xunroll=20' \
CXFLAGS=$(CFLAGS) \
LDFLAGS='$(LDFLAGS) -lpthread' \
opt='$(opt)' \
crafty-make
Compile Benchmark Results
So how did it go? How did the Sun compiler perform? Well come back in a day or so and see the benchmarks. Meanwhile, you might enjoy reading about how the previous comparison between Intel icc and gcc tests went, which you can find here.