Linux
Dropbox and EncFS – Encrypting Local Files
by admin on Mar.22, 2011, under Linux
I have been using Dropbox for quite a while, and I’ve found it extremely helpful. Spideroak, a similar service, is also very interesting and something I am test driving now as well. Being able to share files so easily amongst numerous devices and via the web is handy in the extreme. You can even tie in things like Nevernote into this and sync your notebooks yourself between your devices.
With any of these solutions, security is of course a concern. Regardless of if the data is encrypted in transit, or if the provider encrypts it on their server, I wanted to also encrypt it locally. This is where a combination of Dropbox + encFS comes into play very nicely.
There are many options when it comes to file encryption, but encFS really shines in some areas. Encryption is per-file, and no dedicated space need be reserved before hand. Setup is very simple, and encFS is well supported on all major Linux distros.
Using this solution, encFS stores encrypted files in a Dropbox directory. This is then mounted via encfs to a local folder where the unencrypted files are made available. When I am done, I can simply unmount this directory, leaving only the encrypted files in my Dropbox folder on the local system, encrypted via encFS with AES or blowfish. The information is also thus encrypted in transit, and additionally encrypted by Dropbox/Spideroak on their side.
Setting this up is very simple and takes just a few minutes. More detailed howtos can be found in the reference section, but here is an encFS in 5 minutes quickstart guide:
Ensure you have fuse and encfs installed via your package manager and that the fuse module is loaded
lsmod | grep fuse
Create a directory in Dropbox which will hold the encrypted files, and a mount point outside of Dropbox where the unencrypted versions will be mounted. (For Spideroak simply create two directories in your home folder and add the encrypted directory in your list of folders to back up in Spideroak.)
mkdir ~/Dropbox/encrypted/ ~/unencrypted
Mount the filesystem:
encfs ~/Dropbox/encrypted/ ~/unencrypted/
Note: provide full paths or at least a ~ prefix to encfs.
The first time you do this encfs will set up the encryption. You may choose your options, set the passwords, etc. A “paranoid” auto-config option is available, and full details for options are in the man page.
Using encFS
Now, simply create and use your files in ~/unencrypted. Normal filesystem permissions apply and the use of these should be completely transparent. Anything stored in this mount point is automatically encrypted, and you will see matching (encrypted) entities in ~/Dropbox/encrypted
When you are done, unmount with:
fusermount -u ~/unencrypted
Cryptkeeper Applet
Cryptkeeper is a systray applet for KDE and Gnome which provides a simple GUI for the creation, importing, and mounting of encFS folders. It is quite easy to use. For Suse 11.4, I simply used the rpm available for Fedora 13. Cryptkeeper is maintained by Tom Morton and the source code is available on his site here
By default it uses Nautilus, though KDE users who prefer Dolphin or another file manager can simply change this in Cryptkeepers preferences.
Cryptkeeper also allows you to view information about an encrypted folder, or change the password. These option are available by right clicking on the folder name in the list of encrypted folders.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EncFS
Setup Guides:
The last link provides this suggestion on auto-mounting using the enfs extpass option and a compiled file containing your password. However, be aware this simply compiles your password into a binary which spits it out to std out when run. You are creating a program that will spit out your password, or if strings is run on it your password is visible. Man encfs suggests directing –extpass to ssh-askpass as another method, and there is also the option to use libpam-encfs.
PAM Configuration:
For a guide on setting up libpam-encfs see:
Can’t rip mp3 with kio slave or K3b – libsndfile error
by admin on Mar.06, 2011, under Linux
Recently I was getting errors when trying to rip mp3 files on my Suse 11.3 box, though it seems this issue affects various distributions using KDE. The solution in my case turned out to be quite simple.
Original error when using K3B or audiocd://
Could not read some_song.mp3: encoding failed
WARNING: libsndfile may ignore -r and perform fseek's on the input.
Compile without libsndfile if this is a problem.
I downloaded and compiled the latest version of lame from Sourceforge – which is the same version as the one I had from Packman – 3.98.4. The version I compiled, specifying no additional options, allows ripping of mp3 files no problem.
Running ldd on the packman (Suse repo) binary, and the one I compiled, show that the pm one is indeed compiled with libsndfile:
Callandor:~ # ldd /usr/bin/lame*
/usr/bin/lame:
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007fff563ff000)
libncurses.so.5 => /lib64/libncurses.so.5 (0x00007fc9202d2000)
libm.so.6 => /lib64/libm.so.6 (0x00007fc92007b000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007fc91fd1b000)
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00007fc91fb17000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007fc920527000)
.
/usr/bin/lame-pm:
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007fff9cfff000)
libmp3lame.so.0 => /usr/lib64/libmp3lame.so.0 (0x00007f84c6fc3000)
libncurses.so.5 => /lib64/libncurses.so.5 (0x00007f84c6d6e000)
libsndfile.so.1 => /usr/lib64/libsndfile.so.1 (0x00007f84c6b07000)
libm.so.6 => /lib64/libm.so.6 (0x00007f84c68b0000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007f84c6550000)
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00007f84c634c000)
libFLAC.so.8 => /usr/lib64/libFLAC.so.8 (0x00007f84c60fc000)
libvorbisenc.so.2 => /usr/lib64/libvorbisenc.so.2 (0x00007f84c5d21000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f84c723f000)
libogg.so.0 => /usr/lib64/libogg.so.0 (0x00007f84c5b1a000)
libvorbis.so.0 => /usr/lib64/libvorbis.so.0 (0x00007f84c58ed000)
Input from other users on the Suse foum shows that this issue is a bit hit and miss. For some, lame linked against libsndfile seems to work okay. For myself and others on various bug reports, not so much. Building lame is very easy though, and should you be experiencing this issue it might be something to try.
Adding JavaScript to a Joomla Article
by admin on Feb.27, 2011, under Linux
The JCE editor has some nice features, including allowing you to insert php and Javascript into an article. There are however several things which may stop this from working. And judging for the huge number of forum posts on this, it seems that getting this to work is very problematic. Here is what I did to allow the use of Javascript in articles:
- Install the JCE editor plugin
- I recommend uninstalling, or at least disabling, any other PHP / Javascipt editor plugins (Jumi, Sourcerer, etc.) If these are active they tend to compete with each other. Simplify.
- Use the JCE configuration manager to grant permissions to the needed groups
- Configure JCE – set cleanup HTML to no
- In JCE group configuration settings: Allow PHP and Javascript
- This post was the hinge-pin of my issue. Ensure that the default content filter in Joomla is not set to clean content tags! By default in Joomla 1.5.8 even content added by Superadmin is cleaned.
- Navigate to Content → Article Manager.
- Press the Parameters icon in the toolbar to show the Articles – Global Configuration screen.
- Scroll down to Filtering Options, highlight all Filter groups except Super Administrator, and select Filter type of Blacklist (Default)
- If content filtering as noted above is active, you may be able to insert, and even preview, code – but when you apply or save the code will be stripped.
Additional things you may need to do:
- Use the show / hide button in the editor to ensure your code is being inserted correctly. You might even need to follow a process of: click show/hide editor > hide > insert js> click apply> click show/hide > show > save
- If html tags are being added when you save, or other weird issue are occurring, try replacing the editor_plugin.js with a patched version from here and clear browser cache.
- Disable any other content / editor plugins that may be interfering to isolate the problem.
Additional info can be found at the JCE forums.
Another source of information on integrating Javascript and CSS can be found here
Compiling libaam.so for EnergyXT2 on 64-bit
by admin on Jan.27, 2011, under IT Adventures, Linux
Recently I decided to revive my interest in playing the guitar. I took a few lessons back around 1988, but didn’t stick with it. Over the years my desire to pick it up again has cropped up here and there, but either I was too busy with life and college, or my guitar was in another state, or whatnot. However, I was recently reunited with my guitar, but not my old amp. I decided to see how I might use my Linux box to allow my to play through it, and perhaps have some effects processing as well. I quickly discovered the rich extent of audio tools available for Linux, and even for the guitar specifically. I hit a gold mine.
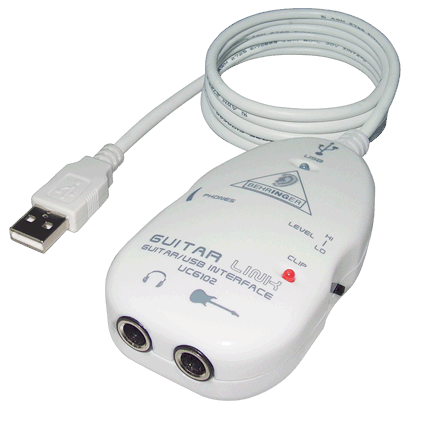
I quickly found several USB sound cards with 1/4″ jack inputs, which were well supported under Linux, were readily available – and at a modest price. I ordered a Behringer UCG 102 off Amazon for all of $29.
I also discovered Rakarrack, an full featured guitar effects processing suite for Linux. I had no issues getting Rakarrack installed, and anxiously awaited the arrival of the new sound card. If you play the guitar, you really have to check out Rakarrack – it is amazing.
When the Behringer arrived I was shocked to discover the EnergyXT2 recording software it came with nativity supported Linux. Displayed right on the CD sleeve was a an nice capital “L” and advertised Linux support:
This, of course, I would have to try – simply as a matter of principle. I soon discovered however several issues with this software, and my solutions to them are below.
NOTE: I should say however that the Behringer Guitar to USB interface worked flawlessly, and in short order I had connected my guitar, fired up the Jack audio server, launched Rakarrack and was playing. The effects provided by Rakarrack include: distortion, chorus, reverb, flanger, digital delay and many others. Wow – this is like having an array of effects pedals for free, and they sound great. And it should be mentioned as well that the open source Ardour recording software worked without requiring anything beyond finding and installing the RPM. So . . . why even bother with getting EnergyXT2 to work? Well, because it’s there. I loved the idea of getting Linux software with a product I bought, and by God I intended to see it work.
Do you need to do this too? Well, that’s up to you. You can certainly use Ardour to record with, and it works extremely well. But if you want to try out EnergyXT, and use it with Jack, and with MIDI, and especially if you are running 64-bit – then read on.
If all you want is a basic working EnergyXT2 without Jack support, that should not be too difficult:
0) First – you need to download the latest version of EnergyXT2 for the website. The version which was shipped has a bug which caused it to fail returning:
X Error of failed request: BadImplementation (server does not implement operation)
Major opcode of failed request: 139 (MIT-SHM)
Minor opcode of failed request: 5 (X_ShmCreatePixmap)
Serial number of failed request: 382
Current serial number in output stream: 384
X Error of failed request: BadDrawable (invalid Pixmap or Window parameter)
Major opcode of failed request: 55 (X_CreateGC)
Resource id in failed request: 0x2a000a4
Serial number of failed request: 383
Current serial number in output stream: 384
This is easily solved by downloading the updated version. You might want to grab the manual too.
At this point it should start and work correctly, but you will not have Jack support. For that you need to continue with the next steps. This assumes some familiarity with compiling things, obtaining required libraries, and some basic debugging – it is not really difficult, but if you have not compiled things much it may be a learning experience.
1) The version of libaam.so provided with the software has several limitations, the most significant of which is that it does not support the Jack audio server. Now – there are two routes to take here:
A) Download the source for libaam.so from the EnergyXT libaam site and compile using the instruction there, or:
B) Download and compile the source for from the libaam Jack Sourceforge project. This is most certainly the better route to take as it supports more MIDI channels and also can build a QT Interface to configure it to work with Jack. Simply download, untar and continue with the steps below. Note this contains its own readme and make file, and QT interface, unlike the basic version for the EnergyXT site.
2) Next, I was building this on a 64-bit OpenSuse 11.3 system. The fact of building this on a 64-bit platform introduces a number of additional factors which have to be addressed. If you were to build this on a 32-bit platform, it would be easier. If using a 64-bit environment (perhaps like Studio64) the first thing you need to do is ensure you have the 32-bit versions of the libraries you will need, AS WELL AS 32-bit versions of gcc, glibc, etc. These are going to be called different things depending on your distro, but you are looking for things like:
libasound2-devel
libjack-devel-1.9.5-2.8.i586 (get 32-bit version from webpin)
alsa-plugins-jack qjackctl
libqt4-devel-4.6.3-2.1.1.i586
alsa-devel-1.0.23-2.12.x86_64
glibc-32bit-2.11.2-3.3.1.x86_64
gcc45-32bit-4.5.0_20100604-1.12.x86_64
gcc-c++-32bit-4.5-4.2.x86_64
And maybe . . .
libSDL_mixer-1_2-0-32bit
libSDL_mixer-1_2-0
Should you receive any build errors complaining about libs you know you have, may need to make some symlinks for several of the libraries, such as:
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/libasound.so.2.0.0 /usr/lib/libasound.so
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/libjack.so.0.1.0 /usr/lib/libjack.so
sudo ln -s /lib/libgcc_s.so.1 /lib/libgcc_s.so
Getting all the 32-bit libraries you need may take a few tries – each time you compile you may be presented with some new library needed – but you should be able to work through them and fortunately there are a limited number required.
If you do not have 32-bit gcc, you may get messages similar to:
paracelsus@Callandor:~/energyXT/libaam-0.0.2> g++ -m32 -shared -lasound -ljack jack.cpp -o libaam.so
/usr/lib64/gcc/x86_64-suse-linux/4.3/../../../../x86_64-suse-linux/bin/ld:
i386:x86-64 architecture of input file `/usr/lib64/gcc/x86_64-suse-linux/4.3/crtbeginS.o’ is incompatible with i386 output
This is simply due to missing the proper gcc and g++ 32-bit packages – oops. (While I had the necessary 32-bit libs for qt and Jack, I inadvertently had not installed 32-bit gcc and g++ libs, so it indeed was missing the 32-bit version of crtbeginS.o, just like it says.
2) This then allowed libaam.so to build, and you should be able to use the library at this point. You most likely want the configuration interface too, but building xt2-config failed with a missing qmake-qt4, though it was installed. That was corrected with a symlink:
ln -s /usr/lib/qt4/bin/qmake /usr/bin/qmake-qt4
3) The next problem building xt2-config was with it expecting a 32-bit build environment – Note that -m32 is specified in the Makefile for libaam, but NOT in the config/Makefile for xt2-config, thus:
g++ -c -m32 -pipe -g -Wall -W -D_REENTRANT -DQT_GUI_LIB -DQT_CORE_LIB -DQT_SHARED -I/usr/share/qt4/mkspecs/linux-g++ -I. -I/usr/include/QtCore -I/usr/include/QtGui -I/usr/include -I. -I. -o moc_configw.o moc_configw.cpp
g++ -o xt2-config main.o configw.o moc_configw.o -L/usr/lib -lQtGui -L/usr/lib -L/usr/X11R6/lib -lQtCore -lpthread
/usr/lib64/gcc/x86_64-suse-linux/4.3/../../../../x86_64-suse-linux/bin/ld: skipping incompatible /usr/lib/libQtGui.so when searching for -lQtGui
/usr/lib64/gcc/x86_64-suse-linux/4.3/../../../../x86_64-suse-linux/bin/ld: skipping incompatible /usr/lib/libQtGui.so when searching for -lQtGui
/usr/lib64/gcc/x86_64-suse-linux/4.3/../../../../x86_64-suse-linux/bin/ld: skipping incompatible /usr/lib/libQtGui.so when searching for -lQtGui
/usr/lib64/gcc/x86_64-suse-linux/4.3/../../../../x86_64-suse-linux/bin/ld: cannot find -lQtGui
Now, I can see that g++ is not being called with -m32 when it links the three compiled files main.o configw.o moc_configw.o To get this to build correctly I modified the Makefile in config/Makefile (which is called from the Makefile in the build root), and added:
#CFLAGS = -pipe -g -Wall -W -D_REENTRANT $(DEFINES)
CFLAGS = -m32 -march=i386 -pipe -g -Wall -W -D_REENTRANT $(DEFINES)
#CXXFLAGS = -pipe -g -Wall -W -D_REENTRANT $(DEFINES)
CXXFLAGS = -m32 -march=i386 -pipe -g -Wall -W -D_REENTRANT $(DEFINES)
And . . .
####### Build rules
all: Makefile $(TARGET)
$(TARGET): ui_config.h $(OBJECTS)
$(LINK) $(LFLAGS) $(CXXFLAGS) -o $(TARGET) $(OBJECTS) $(OBJCOMP) $(LIBS)
The result is a working libaam.so you can copy to your energyXT folder (backup and replace the existing) which supports Jack, and a working xt2-config (move it from config/ to /usr/bin)
Of course on a 32-bit OS EnergXT2 should just run out of the box (as long as you have downloaded an updated copy) but you still would not have Jack support (which is really the way to go), or the QT config interface, and as more users move to 64-bit and RT kernels for audio applications, this may come in handy.
PHP Bug 53632 Floating Point Arithmetic Issue and Solutions
by admin on Jan.06, 2011, under Linux
Today the above PHP bug was pointed out to me, and in looking into it further I discovered a few interesting things, which I’ve decided to list here. While this bug is serious, a bit of research quickly showed it requires a rather specific combination of PHP version, OS architecture and CPU architecture and feature set, as well as PHP build options.
1) This is completely dependent on an x87 FPU design flaw, wherein 80-bit FP arithmetic is used.
2) Newer processors (x86-64) with SSE2 are IEEE-754 compliant, and use 64-bit FP. So, even if you are running an affected version of PHP (5.3.x or 5.2.x) on a 32-bit OS, if you have an X86-64 CPU you may not in fact be affected (depending on how php was built). Test and see by running a simple test such as:
[user@host ~]$ cat phptest.php
<?php $d = 2.2250738585072011e-308; echo $d + 0; echo “\n”; ?>
[user@host ~]$ php phptest.php
2.2250738585072E-308
3) One work around, if you are affected, is to simple have php.ini preload a simple script to detect to handle requests containing the problematic value, as described here.
4) Alternatively, if you wish to compile your own PHP, adding -mfpmath=sse (or -ffloat-store) to your CFLAGS will also resolve this issue.
While at first this bug may cause a sense that great effort will be needed on a sys admins part to update PHP on many servers, investigation and testing may show that little needs to be done. Of course, new packages for PHP 5.3 will soon be available with will correct the issue as well, but the above may assist you in assessing what actions may need to be taken in the interim.